Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Drug Addiction Psychology
Heroin produces a feeling of euphoria a rush and often a warm flushing of the skin dry mouth and heavy feelings in the arms and legs. These psychological approaches suggest that a person uses drugs to fill a terrific void in their emotional lives or as a means of quieting voices of inner conflict.
 Psychology Of Addictive Behaviors
Psychology Of Addictive Behaviors
About half the risk for addiction is genetic.
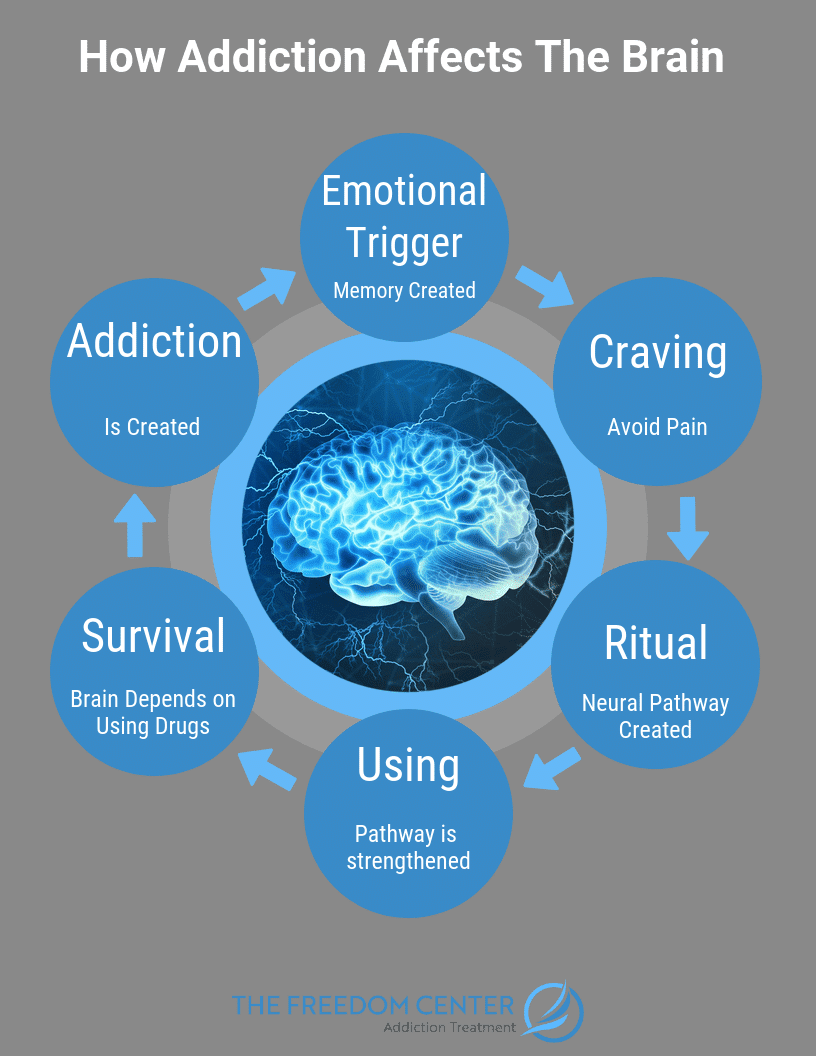
Drug addiction psychology. Genes affect the degree of reward that individuals experience when initially using a substance eg drugs or engaging in certain behaviors eg gambling as well as the way the body processes. According to the American Society of Addiction Medicine ASAM 2011 addiction can be defined as a primary chronic disease of brain rewar d motivation memory and related. All empirical manuscripts are required to report on sex and gender and race and ethnicity of the included samples.
Valerie Ignatenko about her views on drug addiction and recovery. Addictive behavior may include gambling gaming spending sexual activity internet food and substance use. 3 Reviewing a study published in the European Journal of Neuroscience on neural and psychological mechanisms underlying compulsive drug seeking habits the association explained that the want for drugs begins as a goal.
Physical addiction is easy to understand. Strong emotions like rage jealousy fear and hopelessness make some people feel helpless. Addiction is a complex psychological state that is manifested by the use of the compulsive substance despite harmful consequences.
Psychology Definition of DRUG ADDICTION. Treatment for drug addiction has never been a focus area in the discipline of psychology and unfortunately continues to be the case. Brain neurochemistry including the role of dopamine and learning theory as applied to smoking behaviour including reference to cue reactivity.
There are a variety of psychological approaches that can help you recover from your drug andor alcohol addiction and maintain your sobriety. However there are some psychologists and psychotherapists who do work in addiction treatment. A person with an addiction uses a substance or engages in a behavior for which the rewarding effects provide a compelling incentive to repeat the activity despite detrimental consequences.
The one thing that all of these approaches share in common is the concept that you achieve abstinence if you acknowledge your addiction accept your role in the addiction identify and avoid your triggers and make a conscious effort to change your behavior. To that point the Association for Psychological Science writes that only between 20 percent and 30 percent of people who use drugs actually develop an addiction. Risk factors in the development of addiction including genetic vulnerability stress personality family influences and peers.
Addiction involves both physical and psychological aspects. Most psychological addiction begins with feelings that are out of control. THE PSYCHOLOGICALLY INFORMED NEUROSCIENCE OF ADDICTION Addiction involves learned responses to a drug and to the environments in which drug taking is experiencedThe brain encodes these learning histories as neuroplastic adaptations including alterations in the mesolimbic dopamine.
Remarkably the cognitive processes involved in the effects of stress on addictive behavior remain poorly understood. The reversal of helplessness is the psychological function of addiction-Lance Dodes A consequence of this for the treatment of addiction is to focus not on the addictive act itself but on the feelings and events that preceded the very first thought of enacting an addictive behavior when the sense of being utterly trapped arose. Heroin is a very addictive drug processed from morphine a substance extracted from the seedpod of the Asian poppy plant.
Here it is proposed that stress-induced changes in the neural c. Explanations for nicotine addiction. There are psychodynamic attachment theory and self-medication perspectives about addiction to consider as well.
Psychology of Addictive Behaviors is in agreement with the consensus statement on Addiction Terminology developed by the International Society of Addiction Journal Editors. It is well known that stress is a significant risk factor for the development of drug addiction and addiction relapse. The psychology of addiction is a complex pattern of behaviors that lead people to compulsive repetition of a certain behavior even though they know its harmful.
Compulsive dependence on the use of narcotic drugsDrug addiction is characterized not merely by persistent use of. In its simplest form drug addiction can be seen as a way of hacking the brainof finding a shortcut to feelings of emotional reward by bypassing the normal activities that stimulate such. Addiction is a chronic disorder with biological psychological social and environmental factors influencing its development and maintenance.
 Addiction And The Importance Of Belonging The Psychologist
Addiction And The Importance Of Belonging The Psychologist
 The Psychology Behind Addiction
The Psychology Behind Addiction
 The Psychology Of Addiction The Freedom Center
The Psychology Of Addiction The Freedom Center
Psychology Of Addictive Behaviour Antony C Moss Kyle R Dyer Macmillan International Higher Education
Aru Buffalo A Psychobiological Model Of Addiction
 The Psychology Of Addiction The Freedom Center
The Psychology Of Addiction The Freedom Center
 Editorial Board Open Access Journal Of Addiction And Psychology Oajap Iris Publishers
Editorial Board Open Access Journal Of Addiction And Psychology Oajap Iris Publishers
 The Psychology Behind Addiction
The Psychology Behind Addiction
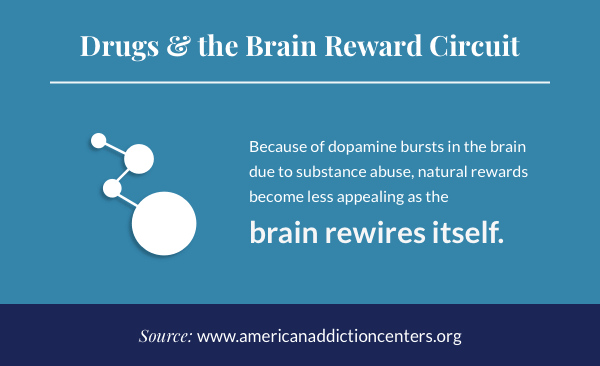 Is Drug Addiction A Disease What Are The Signs Of Addiction
Is Drug Addiction A Disease What Are The Signs Of Addiction
 Addiction Definition Symptoms Withdrawal And Treatment
Addiction Definition Symptoms Withdrawal And Treatment
 Psychology Of Drug Addiction Substance Abuse Disorder Causes Solutions Youtube
Psychology Of Drug Addiction Substance Abuse Disorder Causes Solutions Youtube


Comments
Post a Comment